Extreme rainfall induced risk mapping for metro transit systems: Shanghai metro network as a case
文章作者(*为通讯):
1. Dongming Zhang 1,3,*
2. Hao Bai 1,3
3. Canzheng Zheng 5
4. Hongwei Huang 1,3
5. Bilal M. Ayyub 2,3,4
6. Wenjun Cao 6
作者单位:
1.Key Laboratory of Geotechnical and Underground Engineering of Minister of Education and Department of Geotechnical Engineering, Tongii University, Shanghai 200092, China
2.Center for Technology and Systems Management, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Maryland, College Park, MD,20742, USA
3.International Joint Research Center for Resilient Infrastructure, Tongji University, China
4.Applied Economics Office, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Department of Commerce, USA
5.Jinan Rail Transit Group Co., Ltd, Jinan, China
6.Department of Civil Engineering, the University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
关键词:
Risk assessment; Metro flooding; Extreme rainfall; Multi-layer network; Resilience.
原文链接:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2025.111234
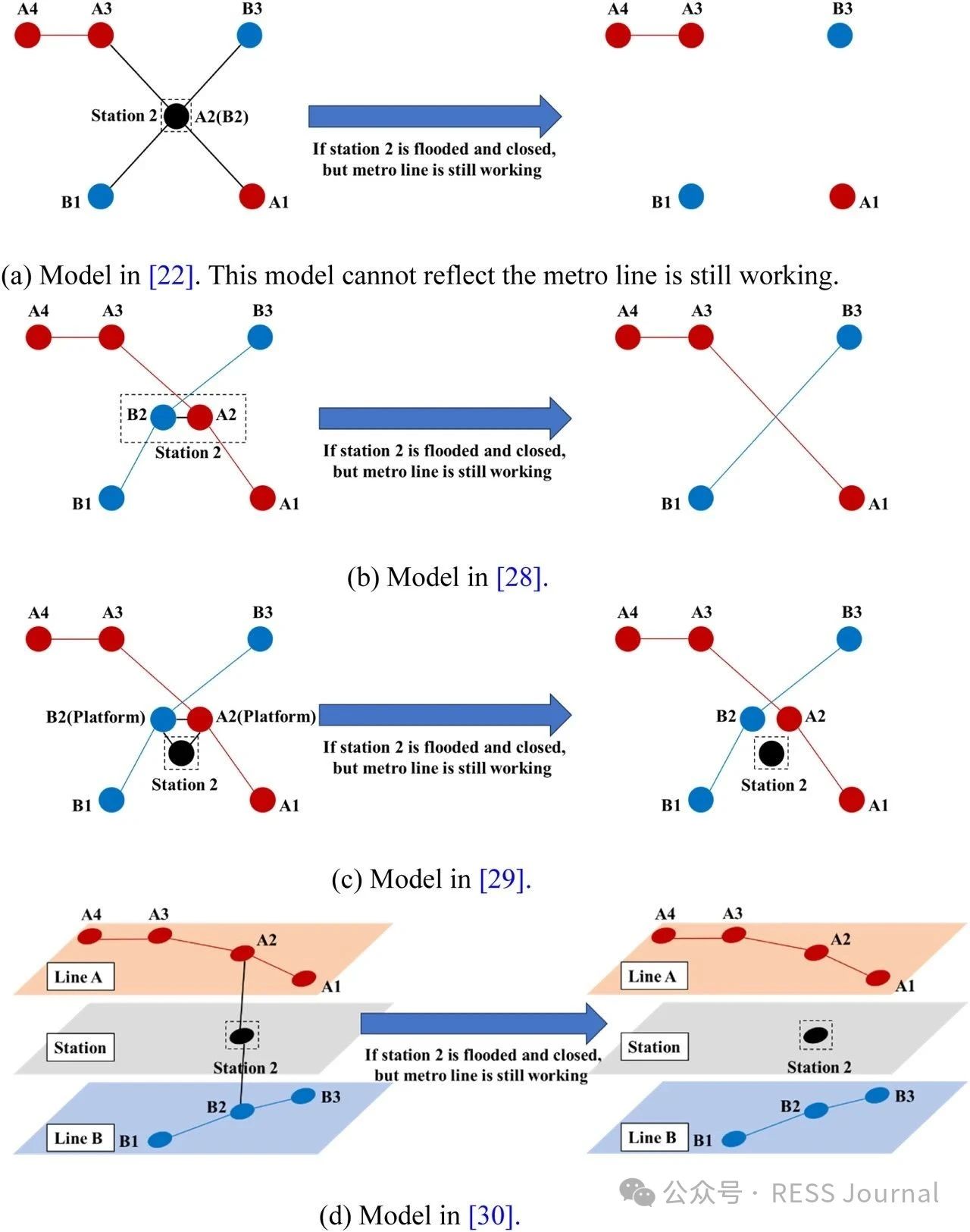
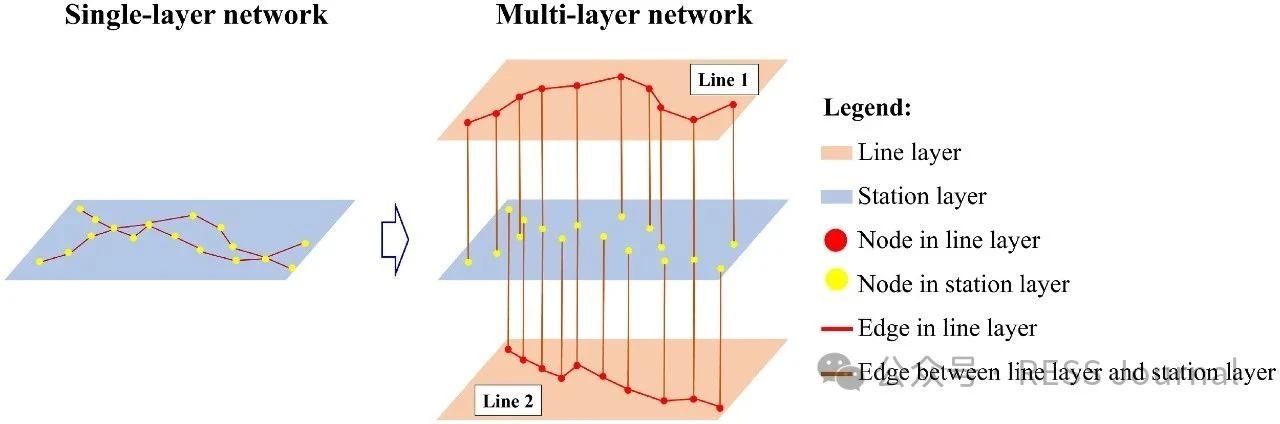
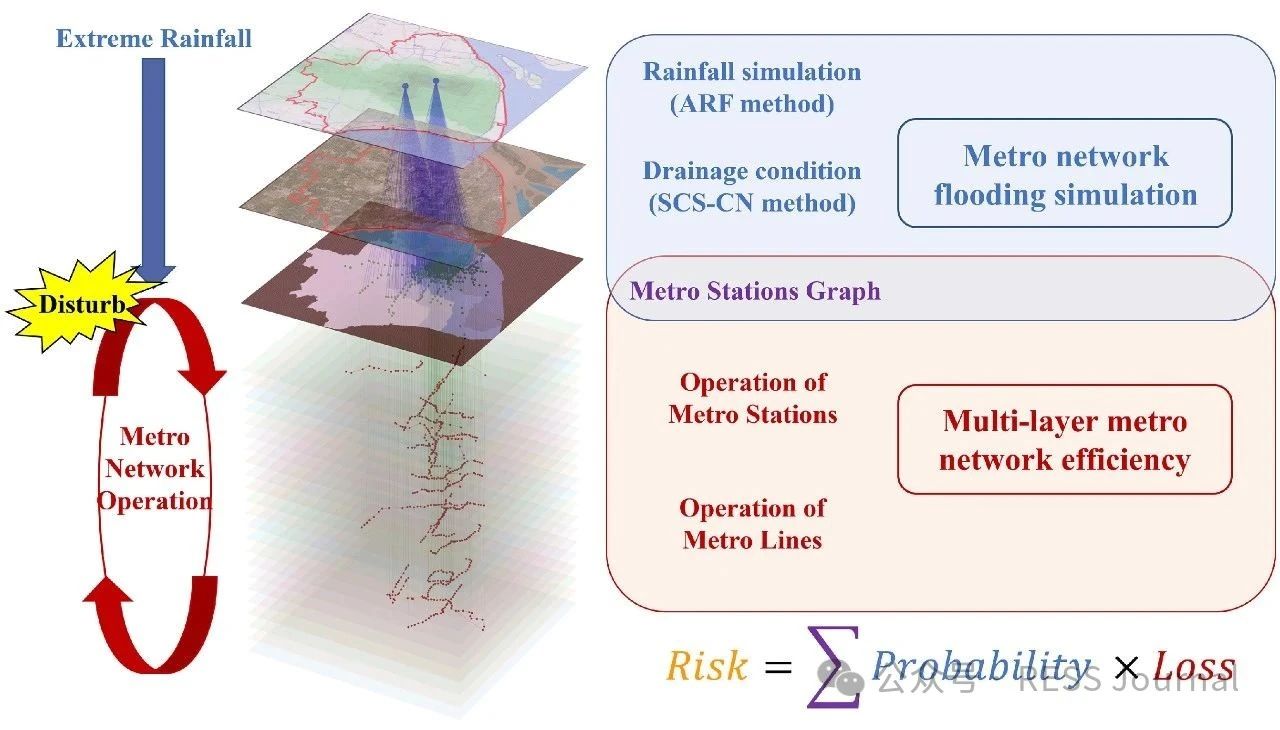
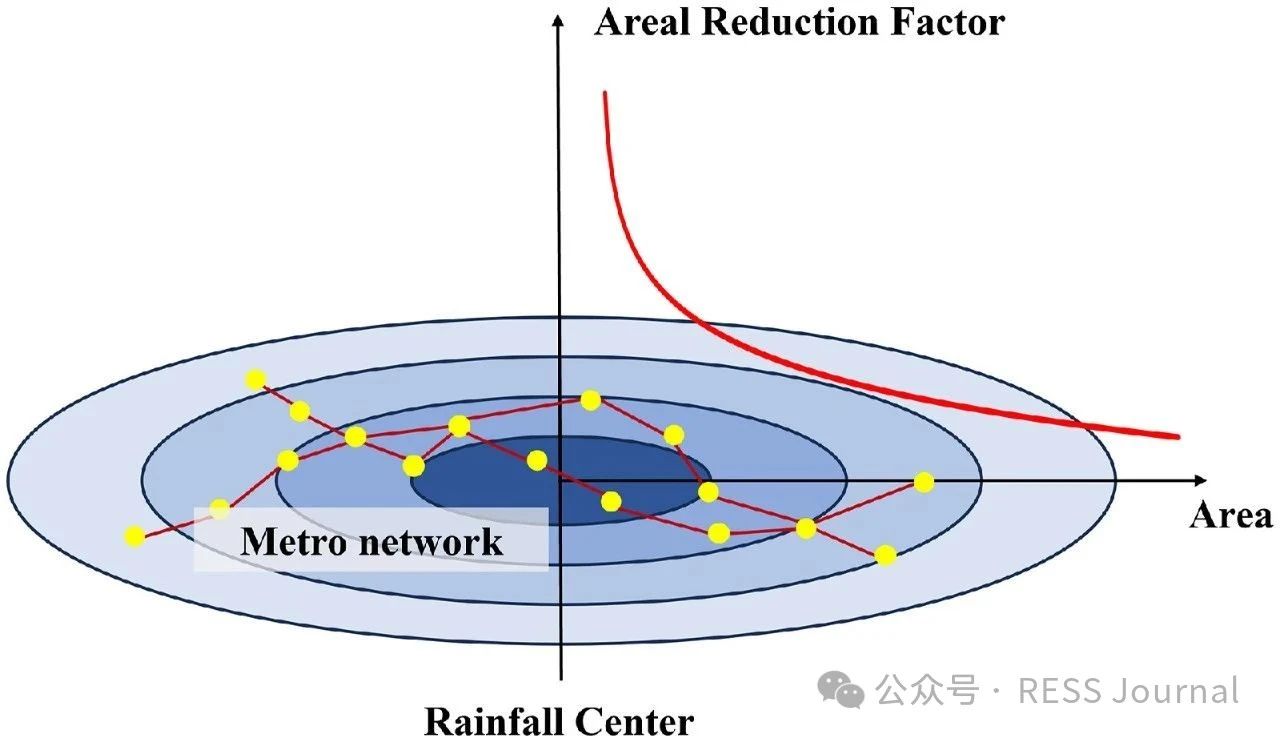
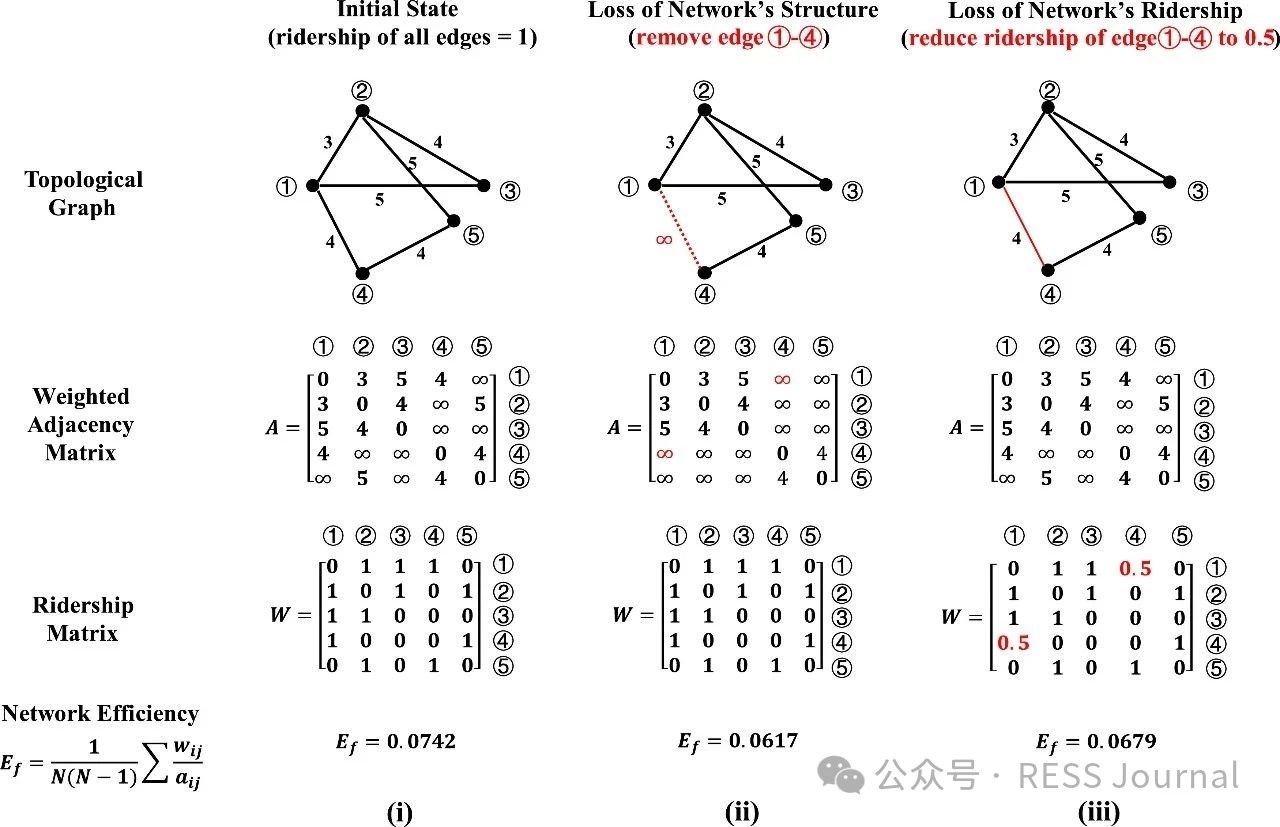
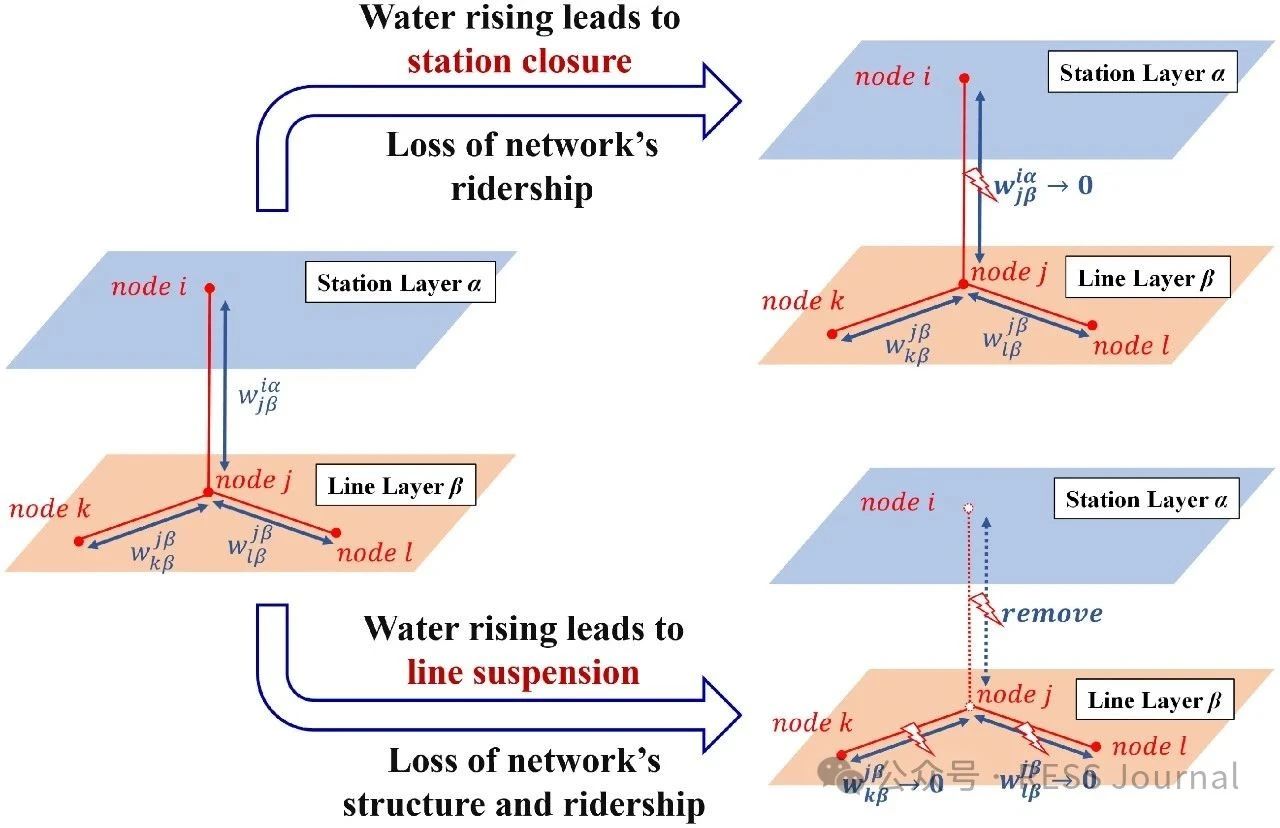

In recent years, a changing climate has induced flood risk as a great threat to the safety and reliability of the metro transit network in mega-cities. A highly networked metro system can lead to a quick spread of this risk, and furthermore, the impact range of single-node accidents of a network is nonlinearly amplified through network connectedness defined by its topology. This study proposes a risk assessment framework integrating extreme rainfall simulation and network loss analysis. The methodology employs the Areal Reduction Factor (ARF) and Soil Conservation Service Curve Number (SCS-CN) to model rainfall-induced flooding, coupled with a multi-layer network-based approach that distinguishes topological interactions between stations and lines. Taking Shanghai metro as an example, this paper highlights its risk follows an exponential distribution to extreme rainfall events, characterized by the finding that nearly 50 % of extreme rainfall events result in <5 % network loss, whereas fewer than 5 % of the events lead to >50 % network loss. When rainfall centers are located in the urban center where metro stations are densely distributed and intricately connected, or when the rainfall intensity and the spatial distribution uncertainty increases, it will pose a greater risk to the metro network.
相关推荐:轨道交通展展位预订 轨道交通展免费报名参观


为保障城市公共交通平稳有序运行,提升公共交通服务品质与可持续性,南昌市强化财政资金保障、创新管理机制,全力支持南昌市公共交通事业健康、可持续发展。2025年,南昌市已累计向南昌轨道交通集团和南昌公共交通运输集团拨付运营补贴5.98亿元,有效推动轨道交通与公交网络的安全、稳定、高效服务。 为实现相关资金使用的规范性、安全性和有效性,南昌市聚焦机制创新,引导建立和完善轨道、公交成本规制办法,支持开展城市轨道交通服务质量评价、南昌轨道交通运营成本规制审计、南昌地铁1、2号线延长线初期运营前安全评估及公交配套衔接方案编制经费等配套事项,不断推动公共交通服务提质增效。(熊孝慧 洪观新闻记者 邬靓)